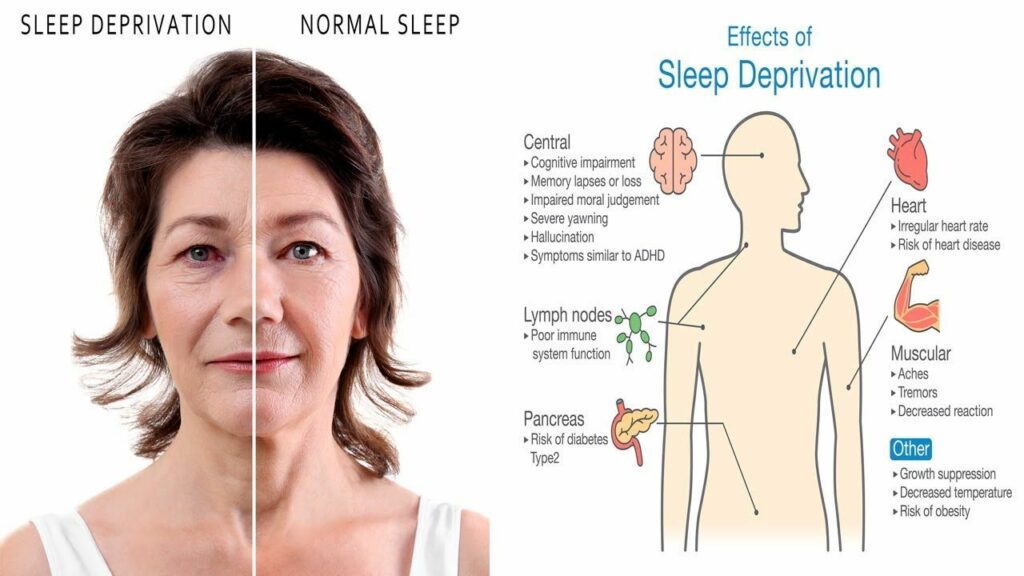
Introduction:
Sleep is a fundamental physiological process that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. However, in today’s fast-paced world, many individuals experience chronic sleep deprivation due to various factors such as work demands, lifestyle choices, and sleep disorders. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the top effects of sleep deprivation on the body, shedding light on the importance of prioritizing sufficient and quality sleep.
Understanding Sleep Deprivation:
Sleep deprivation refers to a condition characterized by inadequate duration or poor quality of sleep. While the exact amount of sleep needed varies between individuals, most adults require around 7-9 hours of sleep per night to function optimally. Consistently falling short of this recommended amount can lead to short-term and long-term consequences for both physical and mental health.
Effects of Sleep Deprivation on the Body:
Impaired Cognitive Function:
- Sleep deprivation can significantly impact cognitive processes such as attention, concentration, memory, and decision-making abilities.
- Lack of sleep can impair problem-solving skills, creativity, and critical thinking, making it more challenging to perform complex tasks and learn new information.
Emotional Disturbances:
- Sleep deprivation can contribute to mood swings, irritability, and emotional instability.
- Studies have shown that individuals who are sleep deprived are more likely to experience symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress.
Weakened Immune System:
- A lack of sleep can compromise the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, colds, and flu.
- Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to increased inflammation in the body, which can contribute to a range of health issues, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders.
Weight Gain and Metabolic Disruptions:
- Sleep deprivation has been associated with weight gain and metabolic disruptions, including an increased risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
- Lack of sleep affects hormones involved in appetite regulation, leading to an increase in hunger and cravings, especially for high-calorie and carbohydrate-rich foods.
Cardiovascular Health:
- Chronic sleep deprivation is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension (high blood pressure), coronary artery disease, and stroke.
- Inadequate sleep can disrupt normal blood pressure regulation, increase inflammation, and negatively affect blood sugar control, all of which can contribute to cardiovascular problems.
Impaired Physical Performance:
- Sleep deprivation can hinder athletic performance and physical abilities.
- Lack of sleep affects coordination, reaction time, and motor skills, leading to decreased overall performance and increased risk of accidents or injuries.
Hormonal Imbalances:
- Sleep deprivation disrupts the balance of various hormones in the body, including cortisol (the stress hormone), insulin (involved in blood sugar regulation), and reproductive hormones.
- Hormonal imbalances can have wide-ranging effects on energy levels, metabolism, mood, and reproductive health.
Increased Risk of Mental Health Disorders:
- Chronic sleep deprivation has been associated with an increased risk of developing mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder.
- Sleep plays a vital role in emotional regulation and maintaining psychological well-being. Lack of sleep can exacerbate existing mental health conditions and contribute to the development of new ones.
Impaired Skin Health:
- Inadequate sleep can affect the health and appearance of the skin.
- Sleep deprivation can lead to increased signs of skin aging, such as fine lines, wrinkles, and uneven skin tone. It can also contribute to the development of skin conditions such as acne and eczema.
Increased Risk of Accidents:
- Sleep deprivation compromises alertness, reaction time, and decision-making, significantly
- increasing the risk of accidents, both on the road and in other daily activities.
– Studies have shown that drowsy driving can be as dangerous as driving under the influence of alcohol, leading to impaired judgment and slower reaction times. 7.2 Cognitive Decline: Prolonged sleep deprivation is associated with an increased risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and dementia. Adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining brain health, supporting memory, and preventing cognitive impairment.
Conclusion:
Sleep deprivation has far-reaching effects on various aspects of our bodies and overall well-being. From cognitive impairments and emotional instability to physical health issues and safety risks, the consequences of sleep deprivation are significant. Prioritizing quality sleep and adopting healthy sleep habits is essential for optimizing our physical, mental, and emotional health. By understanding the detrimental effects of sleep deprivation, we can make informed choices and take steps to ensure that sufficient sleep becomes a priority in our lives. Remember, a good night’s sleep is not a luxury but a fundamental necessity for a healthier and more fulfilling life.